On 23 April 2019, Binance burned 5 million of its own highly valuable Binance coin (BNB) on the Ethereum network.
 This was not an act of self-inflicted financial harm, but the culmination of plans made since the beginning of Binance’s founding to create its own blockchain network with BNB as the base crypto asset.
This was not an act of self-inflicted financial harm, but the culmination of plans made since the beginning of Binance’s founding to create its own blockchain network with BNB as the base crypto asset.
Just burned 5mm ERC20 BNB, commencing swap to the real #BNB.
— CZ 🔶 Binance (@cz_binance) April 23, 2019
History
Binance was founded by Changpeng Zhao (CZ) and launched in 2017. CZ is a prominent figure in the crypto world who has appeared frequently on podcasts, events, magazines, and news sites to promote and explain Binance’s very ambitious vision.
Having launched at the height of interest in the crypto market in 2017, Binance managed to raise $15 million USD within ten days of launching its initial coin offering and has since become one of the best cryptocurrency exchanges in the world. For an in-depth look at Binance’s vast ecosystem, check out our Binance Review.
In its whitepaper, Binance only vaguely mentioned plans to create a decentralized exchange.

When Binance announced the development of Binance Chain officially, over one year ago, it fleshed out these plans more clearly. The Binance Chain would focus on trading blockchain assets with a focus on ‘performance, ease-of-use, and liquidity’.
Since then, development on the new blockchain has been rapid with its public test net stage, where users could try and test network features without risking real assets, starting at the beginning of 2019.
This changed two months later when the Binance Chain main net was launched, producing the first blocks and generating the network’s 200 million native BNB coins.
Main Net Swap
The original BNB tokens were created on the Ethereum network as an ERC20 token and since its creation; millions of BNB tokens have been transferred, burned, frozen, or exchanged.
In order to move the value of the BNB tokens from Ethereum to the Binance Chain, the accumulation of previous burns and freezes of the BNB token that occurred on Ethereum were replicated, which resulted in over 11 million BNB being burned and over 48 million BNB being frozen on the new Binance Chain.

To ensure the continuation of ownership, BNB holders would transfer their tokens to wallets on Binance.com and the equivalent amount of tokens would be created on the Binance Chain for the same owners.
The swap was a signal that the new blockchain was not only live but that the Binance team and BNB holders trusted the nascent network enough to move billions of dollars’ worth of crypto assets over to it.

If there is a critical flaw in the network, there are currently no recovery plans and all these BNB tokens may well lose their value forever. Like every other public blockchain, anyone can view the latest transactions and block data on the Binance Chain Explorer.
Web Wallet
It is possible to interact with the live Binance Chain by creating a web wallet on the Binance DEX website.
Unlike an account on the main Binance exchange platform, the web wallet is a blockchain-based wallet where users generate their own addresses and private keys used to control the account. That means that users are 100% in control and responsible for their own private keys and losing access to them means not even Binance can help you recover whatever was in those wallets.
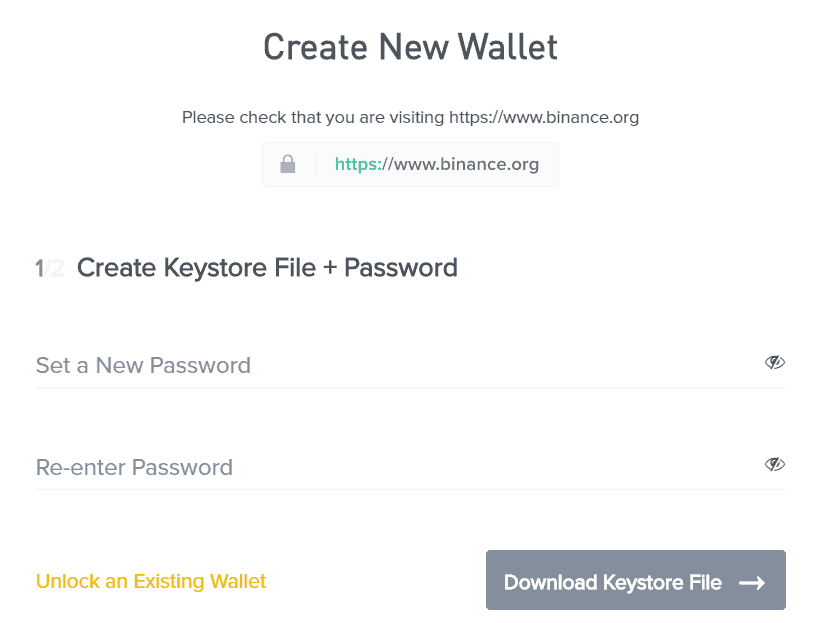
The Binance Chain web wallet can be used to send and receive BNB tokens as well as other crypto assets that are active on the Binance Chain. Besides Binance’s official web wallet, there are other options for users to create a wallet including the hardware wallet Ledger, and mobile apps Trust Wallet and Enjin.

The Binance Chain was launched less than a month ago so it is still very new and the main trading feature that is supposed to be the main function of the network is not yet available. However, the network’s main features can be seen in this preview:
Ethereum Killer?
With nearly every new blockchain launched that is focused on being a platform and not simply a store of value or currency, there are whispers of it being an “Ethereum Killer.” Though the leading smart contract platform has many viable competitors, Binance at least, for now, does not seem to want to be one of them.

On whether the Binance Chain supports smart contracts, the answer from CZ and the official FAQ is a firm ‘No’. Since the beginning, the Binance Chain was meant to focus on being a decentralized exchange and the creation of a new blockchain is meant to be a solid foundation in supporting that focus.
The technology underneath the Binance Chain, however, does not rule out the development of smart contract applications.
It may be something that is enabled in the future or more likely, it will allow new financial or trading specific applications to be developed as opposed to Ethereum, which aims to be a general purpose and decentralized platform for smart contracts.
Centralized Exchanges
Centralized exchanges operate and are in complete control of their own software and platforms. They are entrusted by their users’ to hold assets and execute trades on their behalf. However, they are vulnerable to problems associated with holding users’ funds.
Some of the largest centralized crypto exchanges in the world have lost their user’s funds including Mt. Gox, which was at one time handling over 70% of all Bitcoin transactions. They lost $450 million of their users’ money.
Other popular exchanges, which have been hacked, are Coincheck, which lost over $500 million, Bitfinex, which lost $65 million, and Bitgrail, which lost $195 million. Even without being hacked, a centralized exchange can be vulnerable to losing funds.
For example, the CEO of Canadian exchange QuadrigaCX died and access to millions of dollars’ worth of crypto assets was lost because he was the only one with the private keys. Centralized exchanges require users to trust not only that the managers will act honorably, but that they will act competently.
Still, because of convenience, ease-of-use, customer support, and speed, centralized exchanges like Binance still dominate the market.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
A decentralized exchange (DEX) is one that generally is not controlled by one central authority and is able to function because it is run on a blockchain network. The benefit of a DEX is that no one party controls a user’s funds, which is also known as non-custodial.
By being non-custodial, it means that funds are not vulnerable to hackers or the incompetence of exchange managers. They are also permission-less, which means that there is no need to register to use a DEX so anyone on the planet can do so without revealing any personal information.

DEXes are generally controlled by a set of smart contracts so there is no one party to manage how traders interact or how trades are made. Instead, the logic of the smart contract dictates the transactions.
Trades are executed simultaneously between buyer and seller so funds never leave a user’s account until the trade has been fully executed.
This is why most DEXes have been built on Ethereum because a smart contract language and platform are needed in order to build a DEX. However, DEXes built on Ethereum have many limitations, which include limited speed and capacity, low liquidity, and vulnerability to manipulation.
The Binance Chain has been built to overcome the limitations that are inherent in Ethereum’s current system.
Liquidity Problems
Liquidity is how much money is readily available on an exchange to complete trades. To start a trade, a user will broadcast that they want to sell a certain asset at a certain price. This creates money on the market so users who perform this broadcasting are known as market makers.
When another user agrees to fulfill that trade, they are known as market takers. When there are a lot more market makers by volume than market takers, then liquidity is high.
Having a lot of liquidity is important because it allows trading to happen more smoothly, quickly, and frequently than in a low liquidity situation.
Low liquidity has been a major problem with DEXes that have far less overall trading volume than centralized exchanges.
Liquidity has been such a problem on the 0x protocol, which is a set of smart controls that acts as infrastructure for different organizations to become DEXes on Ethereum, have created an incentive program that gives up to $15,000 for people to build and run their own market-making bots in order to provide more liquidity to the system.
Popular DEXes that seek to solve the liquidity problem are Kyber Network and Uniswap, which both have their own mechanisms for pooling liquidity on Ethereum.

Front-Running Problems
A report has been released by Cornell University that attempts to analyze and quantify the existing front-running problem on DEXes. Front-running takes advantage of Ethereum’s long block times and gas fee transaction structure.
Bots manipulate the market by adjusting their gas rates in anticipation of other traders so that they could jump ahead in the line of transactions and execute their trades ahead of the human traders.
The delay in transactions and use of gas prices is baked into the Ethereum mechanism and is a problem many DEXes on Ethereum must face. All transactions on Ethereum depend on transaction ordering so there is always a possibility to exploit that mechanism.
A Centralized DEX?
The core criticism of the Binance Chain and Binance DEX is that they cannot be truly decentralized because the network is essentially developed, maintained, and controlled by one party; Binance.
This means that decisions and the most influential nodes in the system are controlled by the Binance team, which gives them the power to make unilateral changes to the system and even shut it down or censor certain users if they really wanted to.
This seems to go against core principles of public blockchains such as Bitcoin or Ethereum that promote a diversity of nodes, which control the network but are not controlled by any single party.
However, centralized companies developing their own decentralized blockchains seem to be the trend right now as both Facebook and JP Morgan are creating blockchain products.
Decentralization on a Scale
The focus of Binance Chain is on very specific features that are not available or not possible to be built on Ethereum or other existing blockchain platforms. CZ takes a more practical and less philosophical approach to the centralized vs decentralized debate.
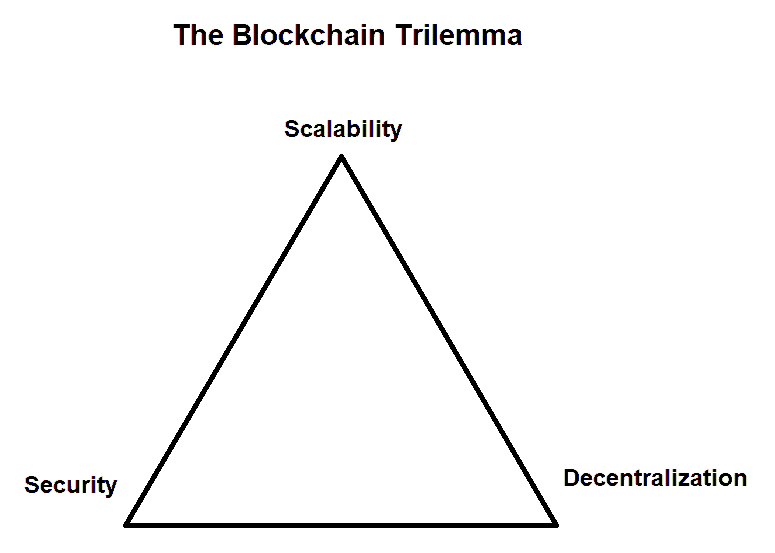
Many blockchains have to deal with the scalability trilemma, and CZ has clearly stated that he believes that:
Best of Both Worlds?
Both centralized and decentralized exchanges have their advantages and disadvantages. By building the Binance DEX in parallel to their main centralized exchange, Binance is able to enjoy the benefits of both.
Binance already has a huge competitive advantage compared to existing DEXes in that they have a highly visible and recognized brand, a large existing user base, and abundant resources for liquidity, development, and business development.
The Binance team also has relevant experience running a successful exchange with a proven and tested business model.

The Binance Chain is an original and standalone blockchain platform. The goal of this new blockchain is to allow users to create new digital assets or tokens, exchange tokens, send and receive BNB tokens, and even stake their own tokens in future governance decisions.
The focus of the Binance Chain is to allow the creation of the decentralized exchange platform, Binance DEX. The Binance DEX solves one of the major problems and vulnerabilities of centralized exchanges, which is holding users’ funds.
The Binance DEX is non-custodial so traders maintain control of their private keys and funds.
The Binance Chain was designed to focus on several core features that solve many of the problems of existing decentralized exchanges. Its aim is to have high speeds for a high volume of transactions and users with the goal of 1 second block times as opposed to Ethereum’s 20 second block times.
It also aims to cut down on the front running and create a user experience that is comparable to its centralized platform.
Binance Chain Infrastructure
BNB as the Native Coin
The original allocation of Binance Coins (BNB) was generated in the form of an ERC20 standard token on the Ethereum network. However, the migration of BNB from Ethereum to the new Binance Chain has been planned since the beginning.
The ownership and total supply of BNB on the Binance Chain will remain the same as on Ethereum, but the BNB tokens will have new features on the new chain. Specifically, they will be used to pay for network transaction fees as well as trading fees directly.
The tokens will also be used as a base asset since it is a native token on the network.

ETH is the base asset and fuel of the Ethereum network and BNB was only one of many tokens on that network. On the Binance Chain, BNB will be the fuel and base asset with the possibility of ETH simply being a token on that network.
As Binance moves toward building a decentralized community, it has plans to incorporate ways to make decisions as a community, which the BNB token will also play a key role.
Tendermint BFT
Every blockchain needs to have a consensus mechanism or way in which the system determines what is true since there are no authorities, managers, or coordinators to handles disputes.
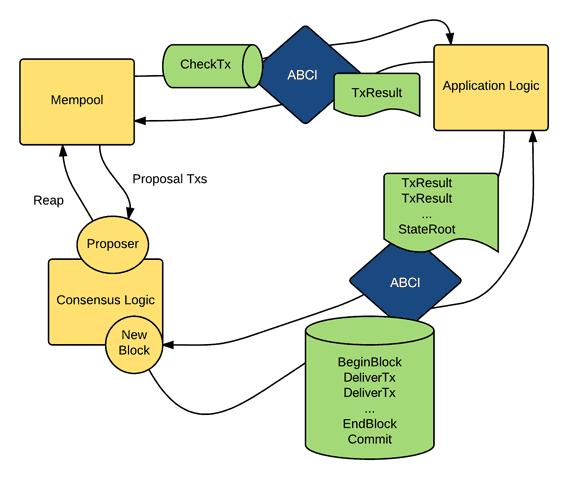
With Binance Chain, the decision-making mechanism comes from its consensus protocol, which is the Tendermint BFT.
What is Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)?
A Byzantine Fault is basically a failure that occurs in a system that needs to coordinate. Generally, most blockchains are decentralized and depend on a group of peers or nodes, which are computers that equally make decisions on the network.
These nodes must all agree or come to a consensus on what is true. A Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) system is one where even if some of the nodes disagree or are malicious, the entire system can go on functioning as normal and reaching consensus.
The system can tolerate, normally, up to one-third of the entire network of nodes disagreeing.
Tendermint is also used by the Cosmos network, which seeks to be the ‘Internet of Blockchains’ or a way to connect different blockchains together. Tendermint is basically a ‘general purpose blockchain consensus engine’ and can be used as a ‘plug-and-play- replacement for the consensus engines of other blockchain software’.
It is thus a very flexible base architecture on which nearly anything can be built on top of including other blockchains such as Ethereum. With this core infrastructure, it means that the Binance Chain is capable of creating general purpose decentralized applications and smart contracts if it decided to. As a reference, you can take a look at our list of 10 most popular Ethereum Dapps in 2019.
Nodes
A node is a peer on a distributed network. Because there is no central database or server, nodes are the computers that keep the network running.

They run the consensus algorithms, produce new blocks, and keep a history of the network’s transactions. The Binance Chain has three types of nodes: witness nodes, validator nodes, and accelerated nodes.
Witness Nodes
A witness node is a full node on the Binance Chain that contains all the data and business logic that has happened on the network. It keeps the history of the network and can communicate with other nodes.
Validator Nodes
Only validator nodes can participate in consensus. They are responsible for validating all transactions on the Binance Chain and are part of the consensus mechanism by voting to produce blocks. They are like miners in Bitcoin and Ethereum or validators in other Proof-of-Stake mechanisms. If you want to learn more, read our guides on all you need to know about Bitcoin mining as well as our guide on how to mine Ethereum.
Not everyone can run a validator node and the initial validators are selected by Binance though plans are for validator participation to open up to more people.
Accelerated Nodes
Accelerated Nodes are a kind of privileged node in the Binance chain. They are faster and more secure and by having accelerated nodes running, the overall transaction speed on the network increases. Binance claims that different organizations are currently owning and running these accelerated nodes.
Trading
The main function of the Binance Chain is for trading. In the Binance DEX, orders are sent to the blockchain itself and executed by the nodes to ensure maximum security and transparency. Orders are filled instantly and funds are automatically moved to the user’s account.
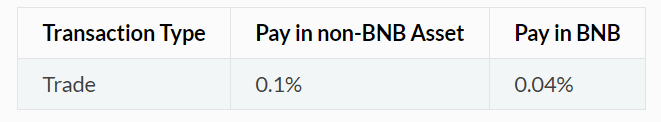
Fees are shared among the validator nodes and charged mainly for trading related actions. Fees can be paid in any asset, but like the normal Binance platform, there is a discount for using BNB tokens to pay for fees.
Asset Management
Another major function and feature of the Binance Chain is the ability to create completely new assets or tokens. The token standard on the Binance chain is called BEP2, which is similar to the ERC20 standard on Ethereum. New assets can be created through the “issue” transaction.
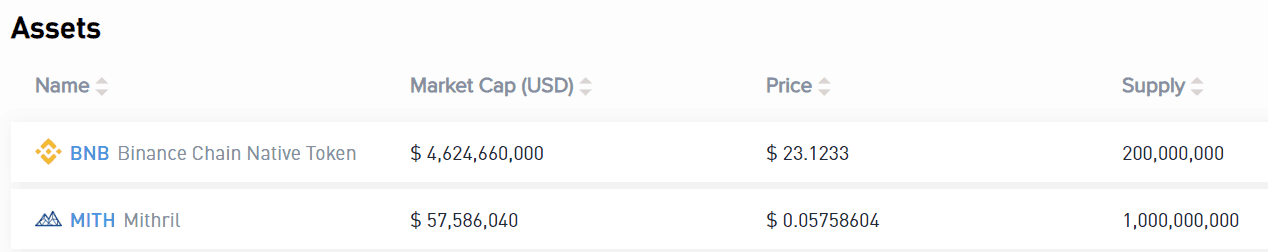
Users can decide things like the total supply, name, who owns the tokens, and whether more tokens can be minted in the future. Once a token is created, it can be minted, burned, frozen, or unfrozen.
As of now, BNB and MITH are the only assets with value on the chain, but more are expected to be added in the future.
Listing Process
Listing a new asset for trade can only be done for BEP2 tokens and the listing proposal needs to be passed by the validators. There is also a fee for listing, which is currently set at 2000 BNB to list a new asset.
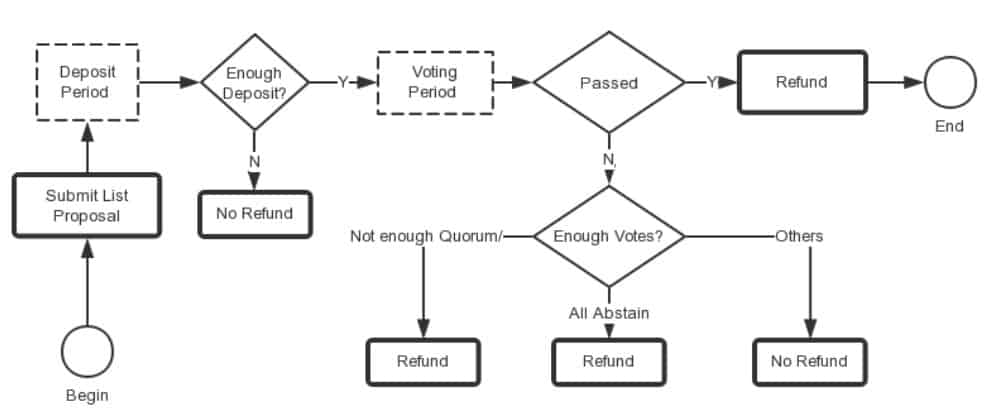
The current on-chain governance mechanism on Binance chain is for adding trading pairs. Basically, anyone can propose to add a new trading pair if they also attach a deposit with it. The deposit is refunded once the proposal has been rejected or accepted.
Ecosystem
Despite not having intentions to become a fully-fledged smart contract system, the Binance Chain is still an open blockchain, meant to be a platform and an ecosystem for other projects to build on top of. In other words, the long-term success of Binance Chain will depend on the quality and number of developers and entrepreneurs building projects on the network.
Mithril
Mithril is a blockchain-based social media content creator system. It rewards content creators with Mithril tokens and is currently valued at over $25 million. Mithril’s MITH token was the first after BNB to be successfully migrated onto the Binance Chain.
#Binance Has Completed the $MITH Token Migration and Has Opened Deposits / Withdrawalshttps://t.co/9EQmBc6Agk pic.twitter.com/f4tsLCxdSG
— Binance (@binance) April 25, 2019
Red Pulse
Red Pulse is another project that has declared its intention to migrate over to the Binance Chain. Red Pulse creates market intelligence reports and is planning to tokenize knowledge on the Binance Chain.

Trendsetting
Binance has been on a roll in recent months. It has opened up fiat-to-crypto gateways such as Binance Uganda, Binance Jersey, and recently Binance Singapore with plans to open up to ten in total with “ideally two per continent.”
It has popularized the Initial Exchange Offering with Binance Launchpad, which has caused many other exchanges to follow suit. And now it has launched its own blockchain network.
Though it is still very early days for the Binance Chain with not even its main trading function enabled yet, the crypto market has been bullish, with the price of BNB reaching all-time highs while other crypto assets remained deflated.
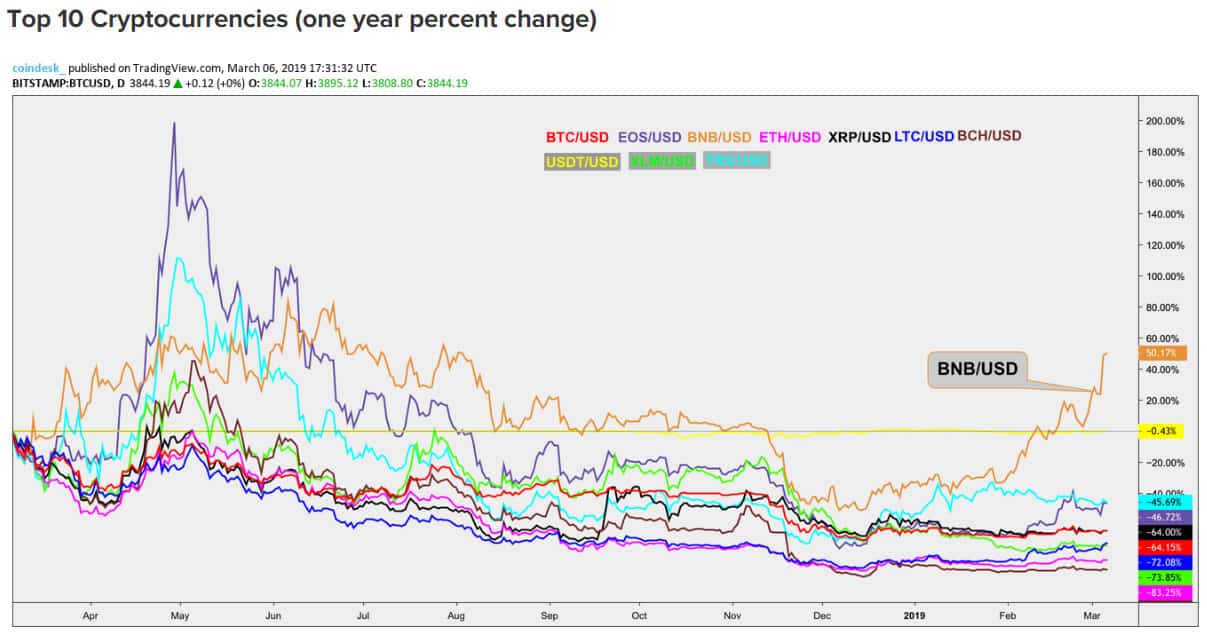
The success of Binance especially in regard to its escalating BNB token value has prompted other centralized exchanges to announce their own DEXes. Huobi plans to invest $100 million in its decentralized exchange and OKEX expects to launch its DEX testnet in June.
With similar advantages to Binance in liquidity, existing users, and experience building effective user experience, it may pose a serious threat, but so far Binance has been able to stay one step ahead.
References
- Binance Fees
- Binance FAQ
- Binance Chain FAQ
- Binance Charity FAQ: Empowering the Bottom Billion with Blockchain Technology
- Trust Wallet Help Center
- Changpeng Zhao’s Twitter Account
- Changpeng Zhao’s Bio
- Binance Whitepaper
- BNB Token Details
- What is ERC20 token?
- Mt. Gox’s Bio
- Mithril FAQ
- Enjin Wallet Support
Disclosure: Blokt strives to provide transparent, honest reviews, and opinions. The writer of this article is a user of the product(s) or service(s) mentioned in this article and was not influenced by the respective owners.
We rarely run ads, but sometimes earn a small commission when you purchase a product or service via a link on our site. Thank you kindly for your support.
Read more or donate here.


![A Beginner’s Guide to Monero – What Is XMR? [Updated 2023]](https://cd.blokt.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Beginners-guide-to-Monero-2-218x150.png)

![Best 5 Bitcoin Sports Betting Sites [2023] (Analyzed & Approved) Best Bitcoin Betting Sites](https://cd.blokt.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/best-bitcoin-betting-sites-218x150.png)

