Going Beyond Currency
When the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin protocol in 2008, a revolution began that goes way beyond currency.

If we can program those assets to behave in any way imaginable, then we can not only redefine the concept and usage of money, we can develop an entirely new financial system.
With crypto-assets firmly established as a valid use case, the industry is now focused on the next phase of building this new financial system: borrowing, lending, and stable currency.
This new area of finance is sometimes referred to as decentralized finance or #DeFi in the Ethereum community. #DeFi does not only include lending, but also exchanges, trading, investing, and any other instrument currently being used in the traditional finance world along with completely novel economic ideas.
The building blocks that have made decentralized finance a possibility are the developments of:
- Crypto assets as collateral
- Smart contracts or decentralized applications (dapps)
- Stablecoins
Crypto Assets as Collateral
Collateral is defined as ‘security pledged for the payment of a loan.’
It is a guarantee that you will do what you say, which in this case is paying back your loan, and if you don’t, you will lose whatever you pledged as collateral.
A very common use of collateral in a loan is a mortgage, where the borrower must use their house as collateral, and that house can be repossessed if the loan is not repaid.
In the ‘real world,’ there are loans that do not require any form of collateral such as credit cards, student loans, or business loans.
These unsecured loans do not depend on guarantees in the form of an asset but rely on a person’s reputation.
People are eligible for credit cards or business loans if they have a good credit history and can generally prove their past reliability in keeping their word.
In Ethereum, like all other decentralized blockchain networks, there is no reputation or personal identity attached to each account. Interactions on Etherum occur under a pseudonym but are not anonymous or untraceable because every transaction is recorded on a globally distributed ledger.
Because of this pseudonymous nature, decentralized loans must use collateral to guarantee loans and crypto-assets such as Ether function as that collateral.
Smart Contracts
Ethereum was designed to be a platform for smart contracts.
Smart contracts are just computer programs like any other, except that by being on a public blockchain, their code and transactions are openly viewable by anyone, they must run exactly as programmed, and they are capable of moving crypto assets.
The main mechanisms of a smart contract are that it executes automatically when certain preconditions are met and that the code or behavior of that smart contract cannot be changed after it has been deployed.
The first two building blocks that make lending on Ethereum possible are smart contracts and crypto assets used as collateral.
By being able to transfer value through the internet using blockchain and by setting it up so that agreements can execute automatically, we are able to have lending. As a simple example, a smart contract can be written with the following conditions:
- Receive 1 Ether from account x
- Send 100 USD Coins (USDC) back to account x
- Receive 100 USDC from account x
- Send 1 Ether to back account x
All of the transactions mentioned above happen automatically so as soon as step 1 happens, step 2 occurs, and as soon as step 3 is triggered, step 4 happens.
“Account x” can be any Ethereum account, but must remain the same throughout the transaction steps. A different account or different borrower would have to start the process from step 1. This is the basic mechanism of a decentralized lending application.
Stablecoins
This leads us to our third building block for decentralized lending, the stablecoin.
Though we can technically lend without a stablecoin, it is enormously risky if the asset that you are borrowing and the collateral that you are putting up as a guarantee both swing wildly in price.
If you borrow $100 this week, you don’t want to have to pay back $200 next week!
Stablecoins are a cryptocurrency that has a stable or constant value over time. It is usually tied in value to a stable fiat currency such as the US Dollar.
Currency Backed Stablecoins
The first widely used and currently most popular stablecoin is Tether. Tether was first launched in 2014 and has a market capitalization of over $2 billion.
Tether uses a basic mechanism to keep its value stable: for every 1 Tether token that is minted or available, there is USD 1 in the Tether organization’s possession. Anyone should technically be able to buy, own, and trade Tether, then be able to redeem that Tether for USD 1.
The past year has seen a massive growth in the number of stablecoins backed by traditional fiat currencies such as USD Coin, TrueUSD, Paxos Standard, and the Gemini Dollar.
These recently launched stablecoins all use the same principle to keep their coin stable, which is to have USD 1 in reserve for each token that they have in circulation.
The downside of this type of system is that users must trust that the organization in control of the stablecoin does indeed possess all the fiat currency reserves that they claim to have. If the value of their reserves falls below the value of their total token supply, then the entire system may become unreliable and collapse.
Tether has been the subject of much controversy in the past about whether it did possess the reserves that they claimed to possess and have very recently admitted that they are not keeping their token 100% backed by US Dollars.
As with anything in the blockchain space, it is best to do your own research and proceed with caution.
Decentralized Stablecoins
One of the biggest advantages of using a public blockchain like Ethereum is that systems can be designed that do not rely on trust.
Simply, the code will execute as programmed and cannot be changed after it has been launched. Therefore, systems can be developed and run without the need for human control or interference.
Besides currency backed or centralized stablecoins, the other type of stablecoin is based on a complex series of smart contracts, which keep the value of the coin constant.
Decentralized stablecoins do not depend on custodians, managers, or auditors to ensure that the price of the coin is steady, but it does depend on trusting that the smart contract code functions as intended.
This trustless principle is what drove the creation of the most popular Ethereum-based stablecoin, DAI, which is developed by an organization called MakerDAO.
Their DAI stablecoin was introduced live in December 2017, and despite a greater than 90% drop in the value of Ether and a consistently increasing supply of DAI, it has maintained its stable peg to the dollar. 1 DAI = 1 USD.
DAI’s remarkable resilience is due to the system of collateral and lending at the heart of the system.
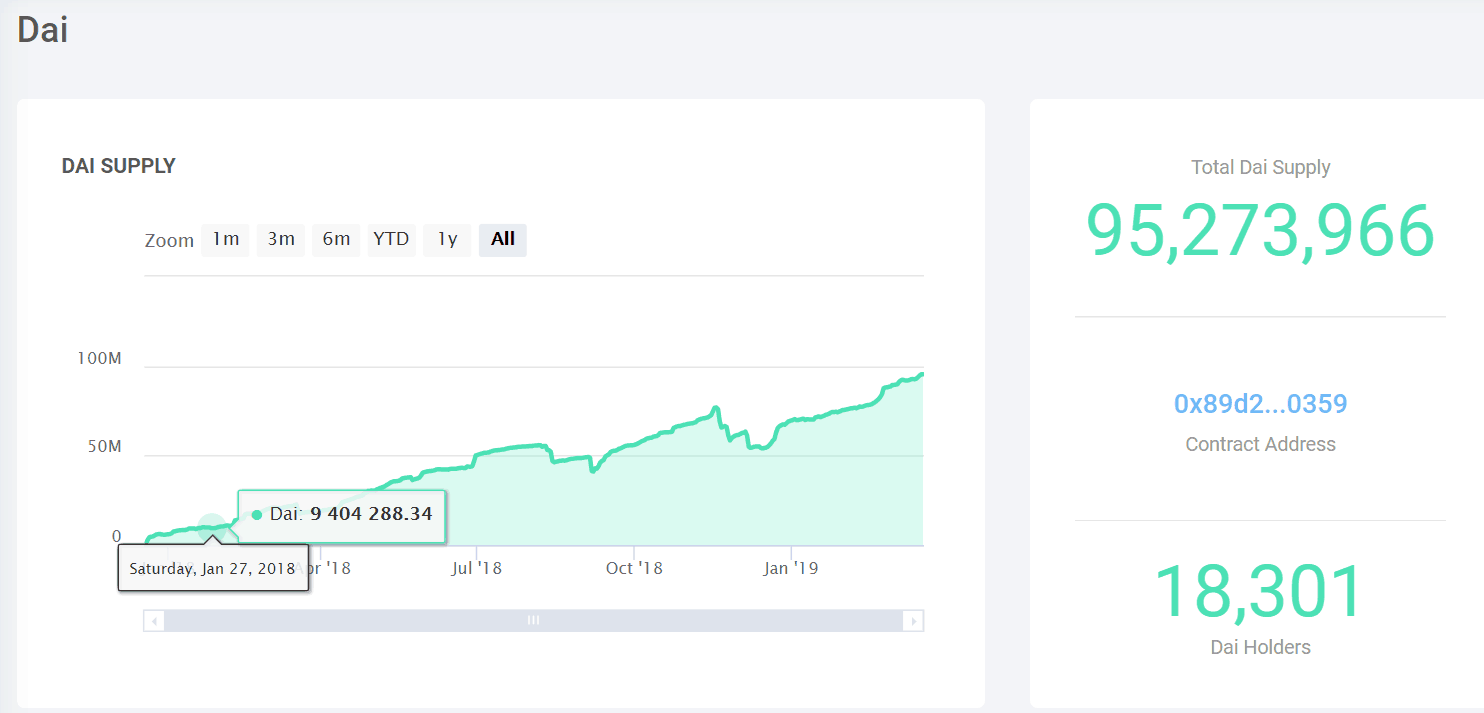
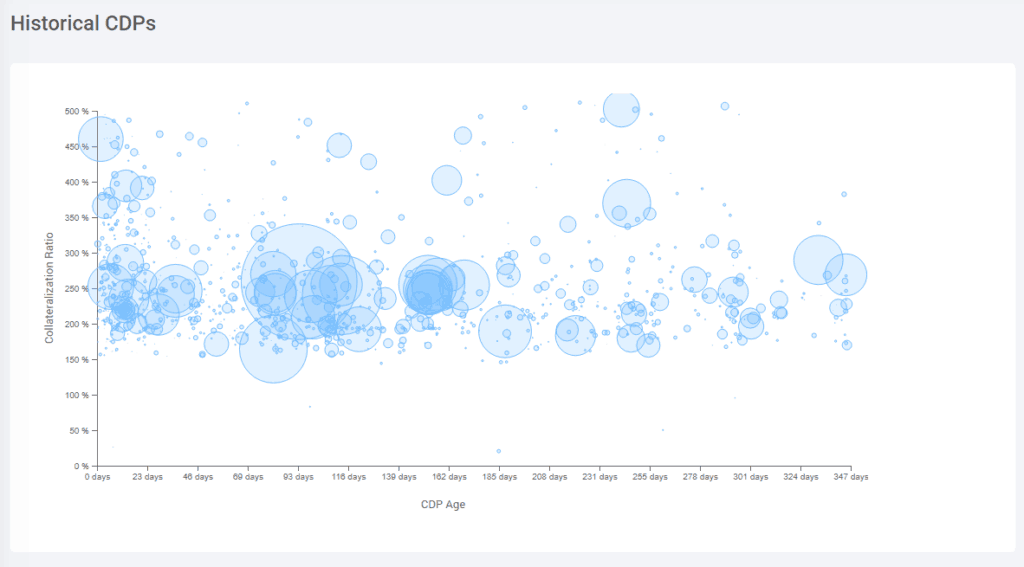
Collateralized Debt Positions (CDPs)
Loans are created and new DAI issued through what are known as Collateralized Debt Positions or CDPs.
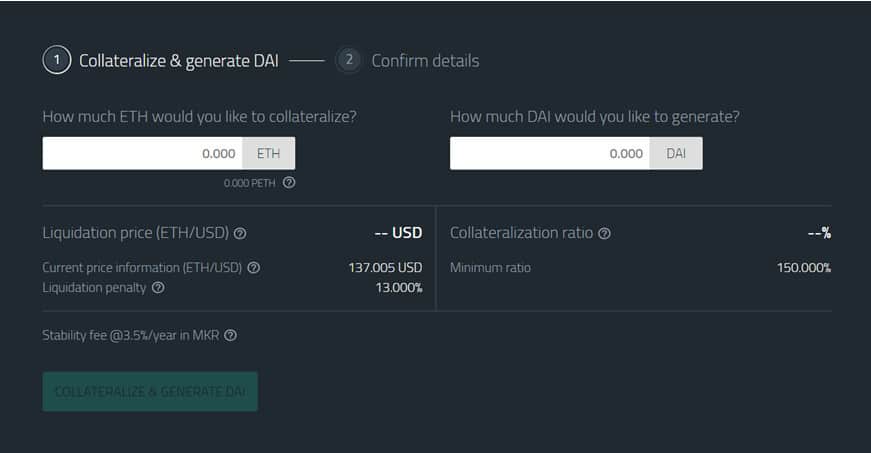
How it works is that anyone who possesses Ether (ETH) can open up a CDP by locking their ETH as collateral and withdrawing DAI as debt. The condition is that each borrower must keep at least 150% of the value of their borrowed DAI in the CDP as ETH collateral.
That means for every $1 that you borrow; you must have $1.50 in ETH locked up as collateral. When the borrowed DAI are repaid, the locked up ETH is returned to the user minus a stability fee or fee for using the system.
If the value of your ETH drops below 150% of what you borrowed, then your ETH is liquidated at the current price to repay your loan plus fees plus penalties. You keep whatever is left over.
The most significant danger of using CDPs is the risk of sudden and large price drops in ETH.
Because this is a completely open system, anyone can see which CDPs were bitten or liquidated, when, and at what ETH price.
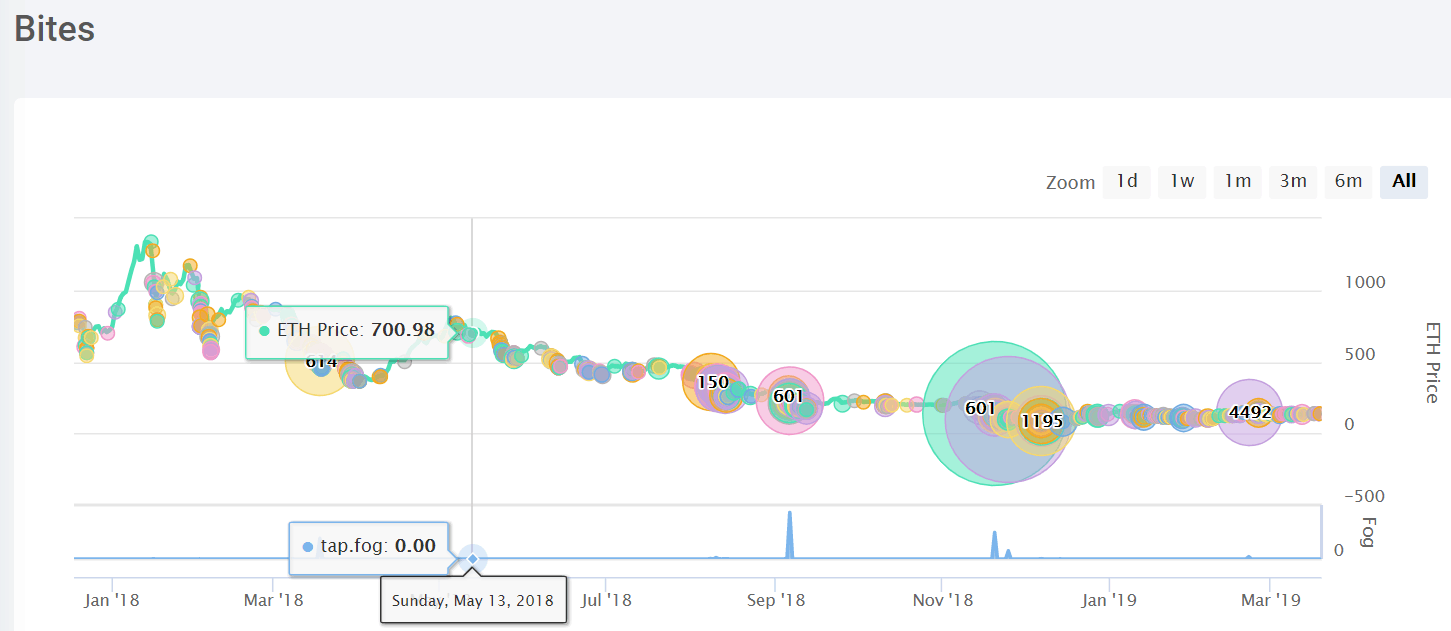
MKR Holders
If MakerDAO is a decentralized system then how are decisions about fees, penalties, and changes made?
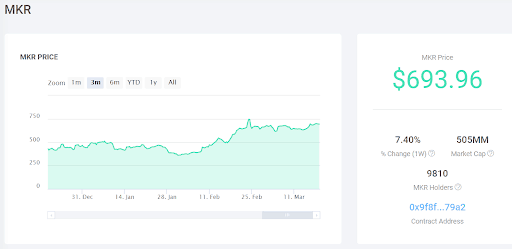
The system is meant to be governed in part by a governance token called MKR that allows holders to both make decisions about the system as well as act as a lever to stabilize the DAI price.
The MakerDAO team originally developed the smart contract system, but since the contracts have been live, they no longer have direct control of them anymore. They guide decision making, but it is the MKR token holders that decide on or vote whether an action should be taken or not.
The process works by first having the MakerDAO team propose a vote and present their reason for why they want MKR token holders to side with them.
For example, during the last increase in the stability fee (fee for opening CDPs), they argued that DAI was consistently hovering at about the $0.975 to $0.985 range for the last 2 months and an increase in the stability fee might bring the price back closer to $1.00.
MKR token holders have voted 5 times to change the stability fee (fee for using CDPs).
Any one party does not centrally control decentralized systems, and they must rely on a system of well-designed incentives, mechanisms, and market forces to keep them functioning.
The lever mechanism of the MKR token is that MKR must be used to pay fees and every time a CDP is repaid, the MKR token is burned or destroyed. This means that increased demand for DAI and CDPs will result in increased demand for MKR and decreased the supply of MKR when CDPs are repaid, effectively increasing its price.
Conversely, if MKR token holders govern the system badly so that CDPs do not have enough collateral, new MKR tokens are automatically created and sold, bringing the system back to sustainable levels, but also effectively decreasing the price of MKR.
Therefore, MKR holders have a monetary incentive to ensure that that the MakerDAO system functions as intended.
Lending in Bear Markets
A bear market is defined in traditional finance as when securities fall 20% or more from their most recent highs, and there is widespread pessimism among investors.
Since crypto assets are so volatile and Ether and other major crypto assets have been down by more than 90% since their latest highs, those in the blockchain community like to call this low period the crypto winter.

The use of lending and borrowing applications have increased during the most recent bear market or crypto winter because many people who are currently holding crypto-assets do not want to sell them while prices are so low.
By using their assets as collateral, holders can spend money while also keeping their positions for the long term.
Borrowing against crypto assets seems to offer the best of both worlds with the only danger being a risk of the collateral’s value dropping too quickly and a loan getting liquidated.
It is why the drop in the price of ETH has corresponded with the increased usage of lending and borrowing dapps.
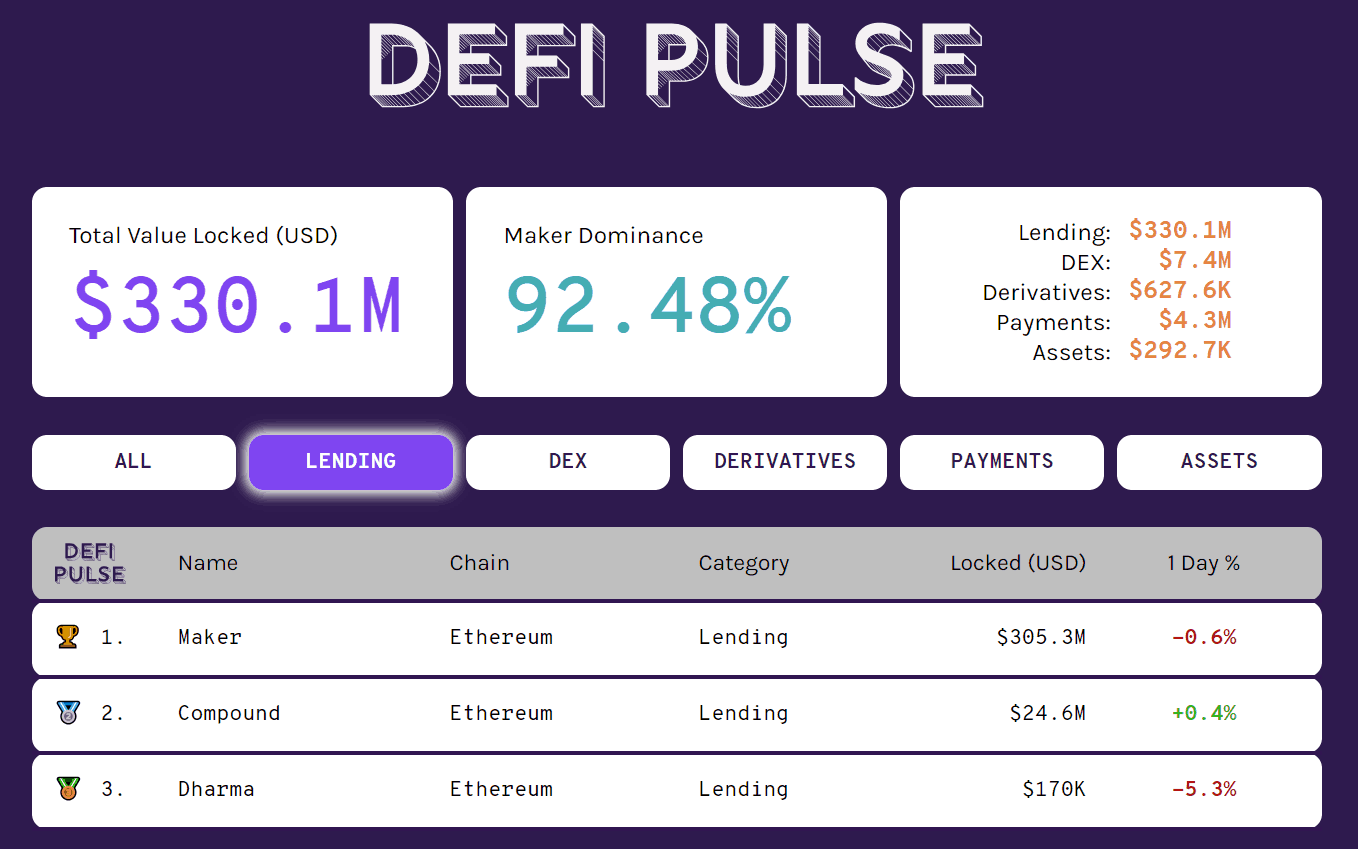
Ethereum Lending Platforms
Here are the leading Ethereum lending platforms:
| SALT | BlockFi | ETHLend | Dharma | Compound | MakerDAO | |
| Registration
Required |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Interest Rate for Loans (Min.) | 5.99% | 4.5% | Market | Market | Market | 3.5% |
| Lend or Borrow | Borrow | Both | Both | Both | Both | Borrow |
| Loan-to-Value (Max.) | 70% | 50% | 50% | Market | 66% | 66% |
| Own Token | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
Centrally Managed Platforms
Some blockchain lending services are managed by organizations, which mean they tend to be more regulated and strict about user requirements than their completely decentralized counterparts.
These platforms hold user’s collateral for them and are able to loan out fiat currencies such as US dollars. The benefit is that in addition to Ether and Ethereum tokens, they also accept other popular cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Litecoin.
They are more compliant with regulations, and they do not operate strictly ‘on-chain,’ which means that their functionality is not entirely dependent on the blockchain or their code and they can have more control and flexibility with their platform.
They are more like a traditional software company or bank that specializes in dealing with crypto assets.
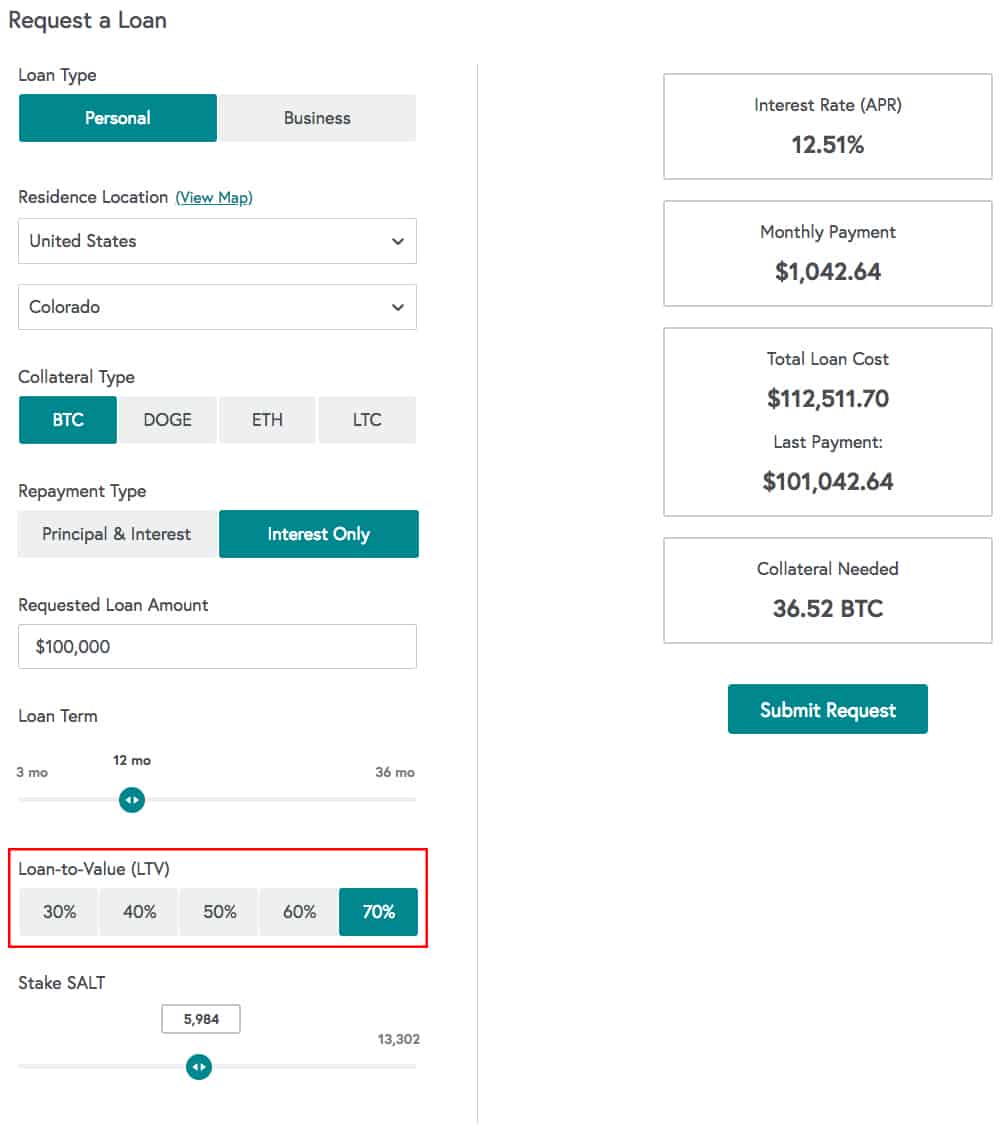
SALT Lending
SALT Lending has its own Ethereum token called SALT, which is used as additional collateral in order to reduce your interest rate and monthly payment.
They advertise an APR starting from 5.99% and loans starting at $5000. You can decide when you pay back your loan, as well as how much collateral you want to provide. Your APR decreases with more collateral and a longer-term loan.
SALT is kind of a bridge to traditional lending in that it provides borrowers with fiat USD loans, tries to conform to regulations, and is limited to certain jurisdictions.
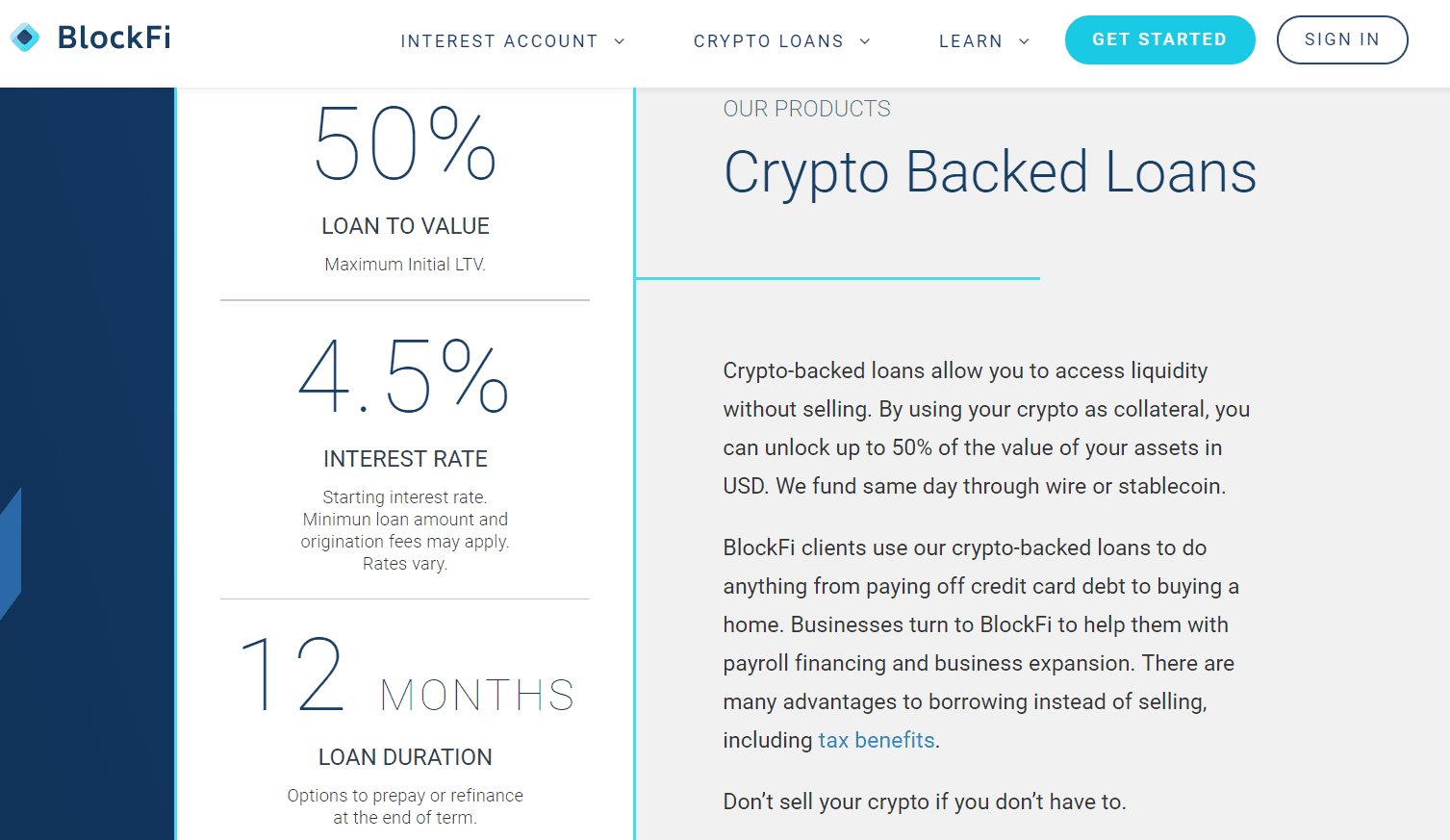
BlockFi
BlockFi is like SALT in that it hopes to link the traditional finance world with the crypto world by offering its lending currency in US Dollars.
It even has a client base of institutional lenders and borrowers. People who want to use their services must create a profile or register.
Users can take out loans for 12 months at a time, and interest rates are as low as 4.5% and a maximum 50% loan-to-value ratio.
In addition to borrowing services, users can also access interest-earning lending options. Users can earn interest of up to 6.2% by depositing their Ether or Bitcoin with BlockFi.
Institutional investors back BlockFi and also has its loans secured by Gemini, a New York trust company regulated by the New York Department of Financial Services, so it is among the most regulated and compliant lenders on this list.
Peer-to-Peer Lending
There are blockchain lending platforms that function as a marketplace where lenders offer loans and terms for loans and borrowers signal the loans and terms for loans that they are looking for.
This type of marketplace is also called peer-to-peer lending, where one user offers to lend money at a certain rate and for certain types of collateral, and other users can either accept or deny their offers.
ETHLend
ETHLend is another lending platform that uses its own Ethereum token, which it calls LEND. Using the LEND token as collateral or the loan currency reduces or eliminates the platform fees.
Like SALT, users must make a profile or register in order to use the platform. You can lend out or borrow ETH, LEND, DAI, or TUSD, and there are over 180 Ethereum tokens that can be used as collateral along with Ether and Bitcoin.

Dharma Lever
Dharma Lever is a decentralized peer-to-peer lending platform on Ethereum. The users set lending and borrowing terms, and the open marketplace determines which terms are accepted or not.
Dharma does not have its own token. The platform is still in alpha mode, which means it has not been fully released so users must register in order to access its services. Even in alpha mode, though, Dharma has over $170K already locked up in its protocol.
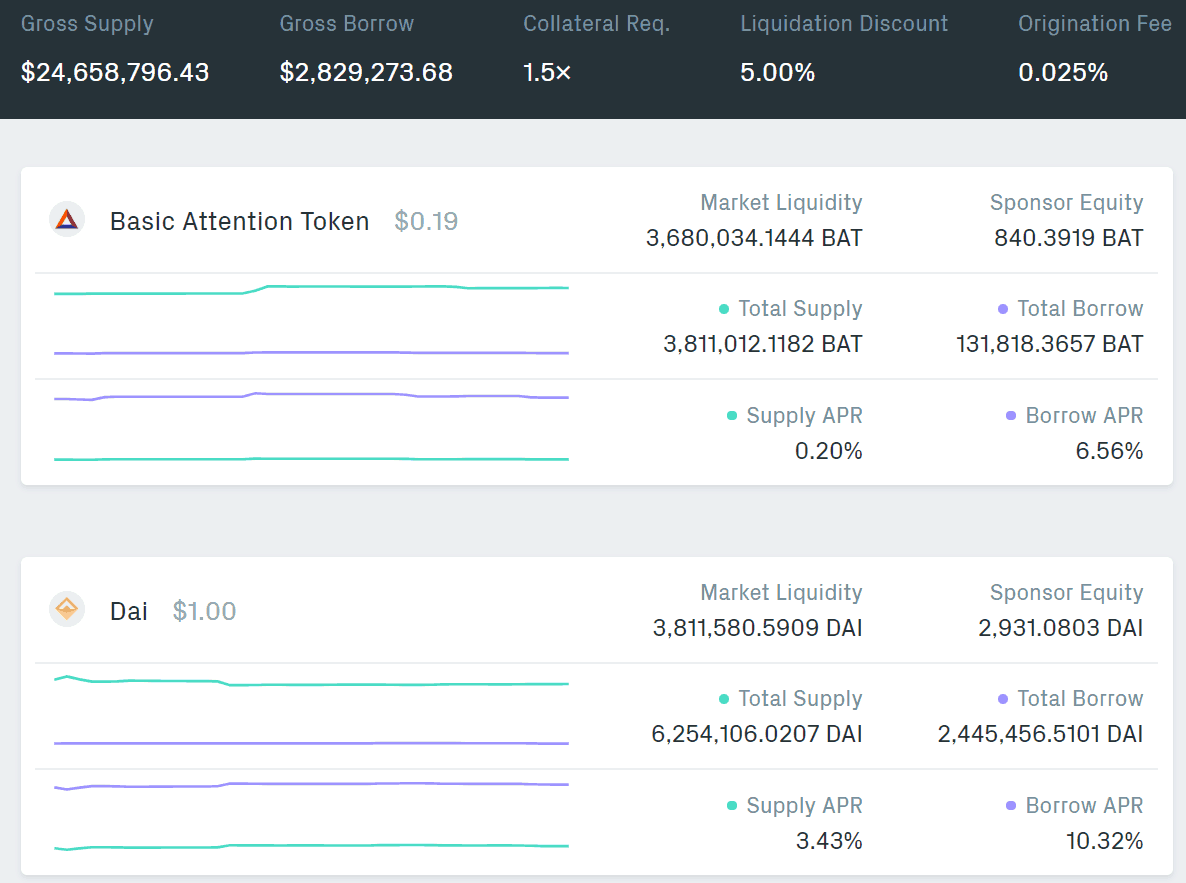
Compound
Compound is currently live on Ethereum and is the second most used decentralized lending application behind MakerDAO.
Like MakerDAO, Compound relies on a completely decentralized system of smart contracts that can be accessed without permission or registration.
Like Dharma, users can set the rates they want to lend out or pick which loans they are willing to accept. You can use Ether and multiple ERC20 tokens such as BAT, DAI, REP, and ZRX to lend out or borrow.
The market forces determine interest rates on the system, and borrowers need to maintain a collateral value that is 150% of what they borrowed.
MakerDAO
Though there have emerged and continue to emerge new ways to borrow and lend money on Ethereum, MakerDAO is by far the most popular decentralized finance application in terms of usage and volume with over 2% of the overall Ether supply locked up in the system’s CDPs.
Their completely decentralized and live smart contract system has been battle-tested through a turbulent bear market with the DAI stablecoin consistently maintaining its peg to the US Dollar.
Currently, users can only lock up Ether and borrow the DAI stablecoin. In the future, they plan to introduce Multi-Collateral DAI, which means that users can lock up a wide variety of assets in addition to Ether including Ethereum tokens, Bitcoin, and anything else that can be tokenized on Ethereum.
Opening your first MakerDAO CDP
- Step 1: Download and install the MetaMask chrome extension.

- Step 2: Deposit or send ETH to your account.
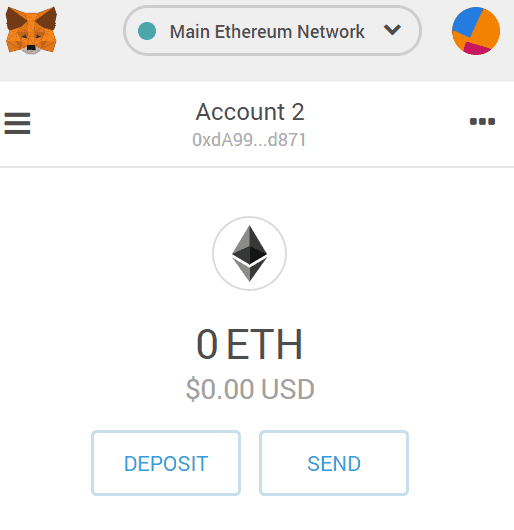
- Step 3: Deposit or send MKR token to your account
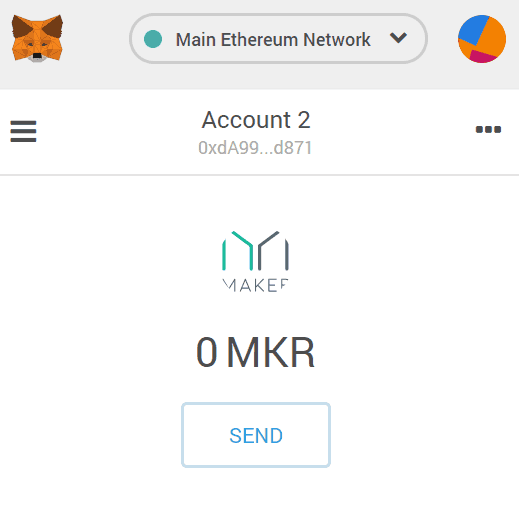
- Step 4: Go to MakerDAO CDP portal

- Step 5: Connect to MetaMask
- Step 6: Open CDP
- Step 7: Decide how much ETH you want to collateralize and how much DAI you want to withdraw/borrow
- Step 8: Withdraw DAI
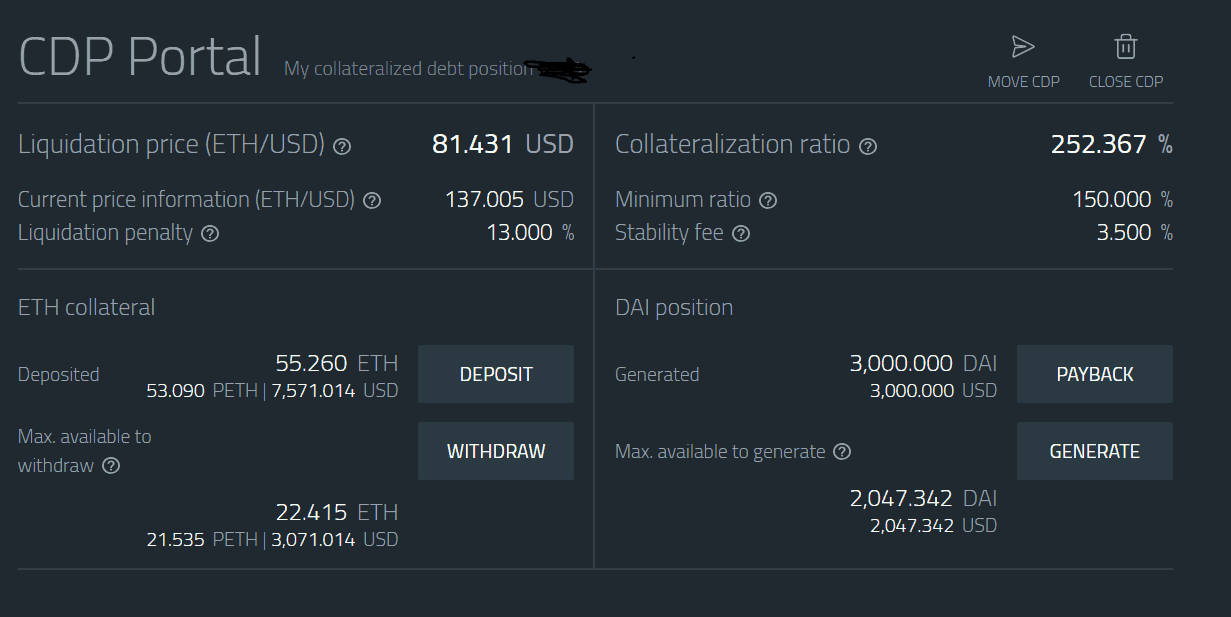
Once you have withdrawn your DAI, you can convert it into your local fiat currency and spend it on your car payments, mortgage, student loans, or anything else you want.
You can also invest the DAI in other crypto assets or hold onto the DAI if you want to hold on to a stable asset because you believe that the price of ETH will go down.
Be careful to watch the price of ETH because if it falls so much that the value of your collateral is worth less than 150% of your withdrawn DAI, your CDP will get liquidated, which means your locked ETH will be sold at the current price to repay your loan.
When you are ready, repay the DAI, and you will receive all of your ETH back minus the stability fee. If ETH goes up, you owe the same amount of DAI, but that DAI is now worth less ETH than when you borrowed it. The opposite happens if the price of ETH goes down.
Congratulations, you have just used your first #DeFi application!
Absolutely anyone with an internet connection and some Ether is able to borrow money and use the platform. This is a completely open, permissionless, global, and decentralized financial system with the potential to change the world.
However, mainstream adoption of #DeFi depends on the industry’s ability to develop simple and intuitive user interfaces, fast transactions, and seamless ways for people to obtain crypto assets.
So, with the user experience still being extremely complicated and slow, and it still being difficult for most people in the world to turn fiat into crypto, we’ve got a long way to go.
References
- Investopedia’s definition of unsecured loans
- Wikipedia’s definition of a stablecoin
- Tether Hired Former FBI Director’s Law Firm by Bloomberg
- Dai CDP user stories on the MakerDAO blog
- SALT expands US reach to 86%
- Dai (DAI) on CoinMarketCap
- MakerDAO’s stability for the blockchain
- Investopedia’s definition of a bear market
- Investopedia’s definition of APR
- The loan-to-value ratio by Wikipedia
- Bitcoin lending FAQs by BlockFi
- Compound’s frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Disclosure: Blokt strives to provide transparent, honest reviews, and opinions. The writer of this article is a user of the product(s) or service(s) mentioned in this article and was not influenced by the respective owners.
We rarely run ads, but sometimes earn a small commission when you purchase a product or service via a link on our site. Thank you kindly for your support.
Read more or donate here.





![A Beginner’s Guide to Monero – What Is XMR? [Updated 2023]](https://cd.blokt.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Beginners-guide-to-Monero-2-218x150.png)

![Best 5 Bitcoin Sports Betting Sites [2023] (Analyzed & Approved) Best Bitcoin Betting Sites](https://cd.blokt.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/best-bitcoin-betting-sites-218x150.png)

